The Problem Docker Solves
The Challenge
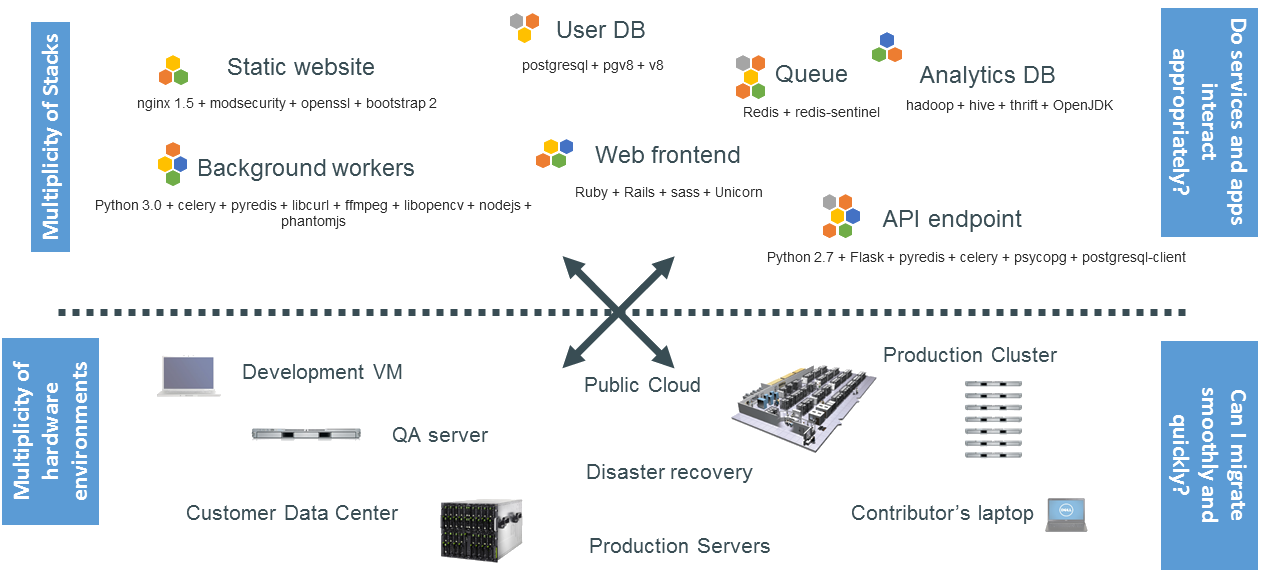
The diagram illustrates the complexity of modern applications, which are composed of many stacks and run across multiple environments. Each component (web frontend, API endpoint, background workers, etc.) relies on different technologies (e.g., Python, PostgreSQL, Redis). These applications must operate across various hardware environments, from development VMs to production clusters, and they need to migrate between them smoothly.
In traditional environments, developers often face the challenge of dealing with dependencies and compatibility issues between development, testing, and production environments.
| Docker simplifies this by providing consistent environments through containers, allowing seamless migration, scalability, and isolation for different services and stacks. |
What about Scientific Computing and Data Science?
The diagram highlights the complexity of modern applications across multiple stacks and hardware environments. This challenge is particularly relevant for scientific computing and data science, where different computational environments (e.g., Python, R, SQL databases) must be reliably replicated across various machines (e.g., development VMs, public cloud, customer data centers).
For example, data science pipelines often rely on specific versions of libraries (e.g., numpy, pandas, scipy) and databases.
| Docker ensures that these environments are consistent across hardware, reducing dependency conflicts and improving reproducibility. |
| In digital twins, Docker helps simulate the same digital model across different environments (like public clouds, local clusters, and IoT hardware) without worrying about differences in software dependencies or configurations. |
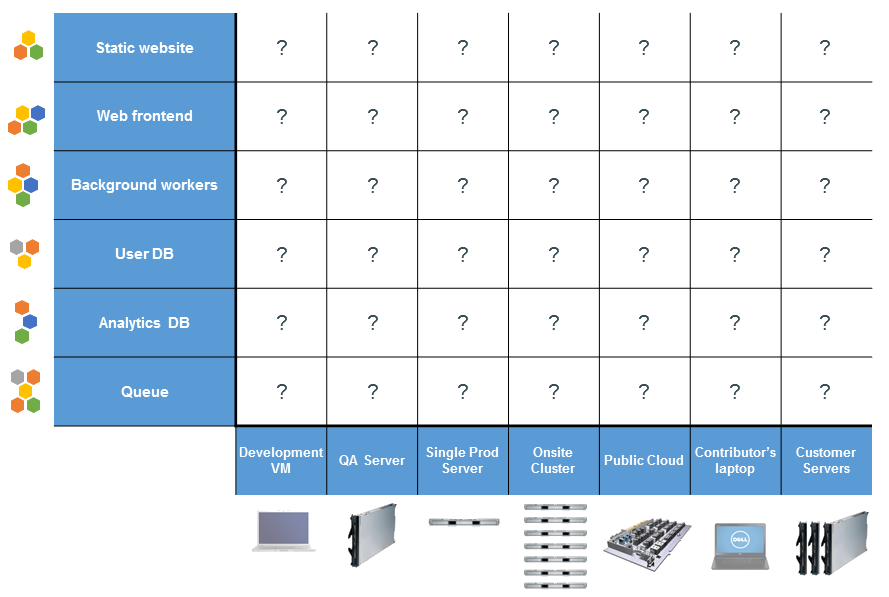
The Matrix From Hell
The image illustrates the complexity of deploying multiple application services (e.g., Static website, Web frontend, User DB, Queue, etc.) across various hardware environments like development VMs, QA servers, public clouds, and customer servers. Each environment may have different dependencies, configurations, and challenges, leading to a "matrix from hell" where managing consistency across environments becomes a difficult and error-prone task.
Managing applications across different environments and platforms can lead to inconsistencies, resulting in delays, bugs, and issues. Docker simplifies this problem by providing a consistent runtime environment.
| Docker solves this problem by providing a consistent, containerized environment across all platforms, reducing variability and improving deployment reliability. |
What about Scientific Computing and Data Science?
The matrix illustrates the challenges of deploying complex, multi-stack applications in different environments. For scientific computing and data science, this often involves managing diverse workloads (data processing, machine learning models, simulations) across environments like local development VMs, QA servers, and public clouds.
| Docker simplifies the deployment of scientific applications and ensures consistency, which is critical for digital twins. These applications require simulating real-world processes with high fidelity across multiple environments. Docker ensures that all dependencies (data processing frameworks, models, etc.) remain consistent, facilitating smooth deployment of digital twin systems. |
 .pdf
.pdf