Docker Architecture
Separation of Concerns
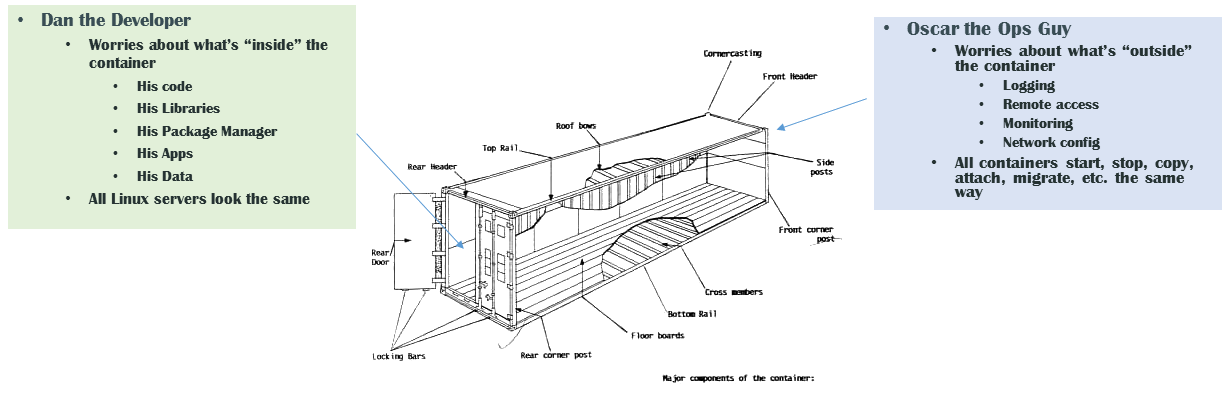
Docker separates the roles of developers and sysadmins by using containers as the interface between these roles.
This concept is particularly valuable for scientific computing and data science, where developers can create isolated environments that encapsulate complex computational workflows, ensuring reproducibility.
For scientific ML and digital twins, containers help streamline model deployment, making it easier to manage models across different computational platforms, from HPC clusters to edge devices.
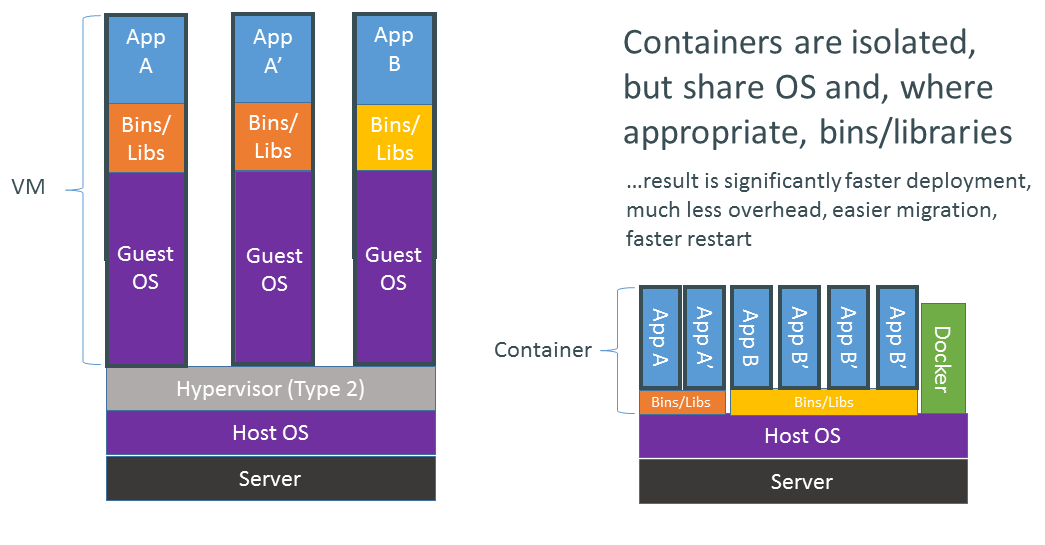
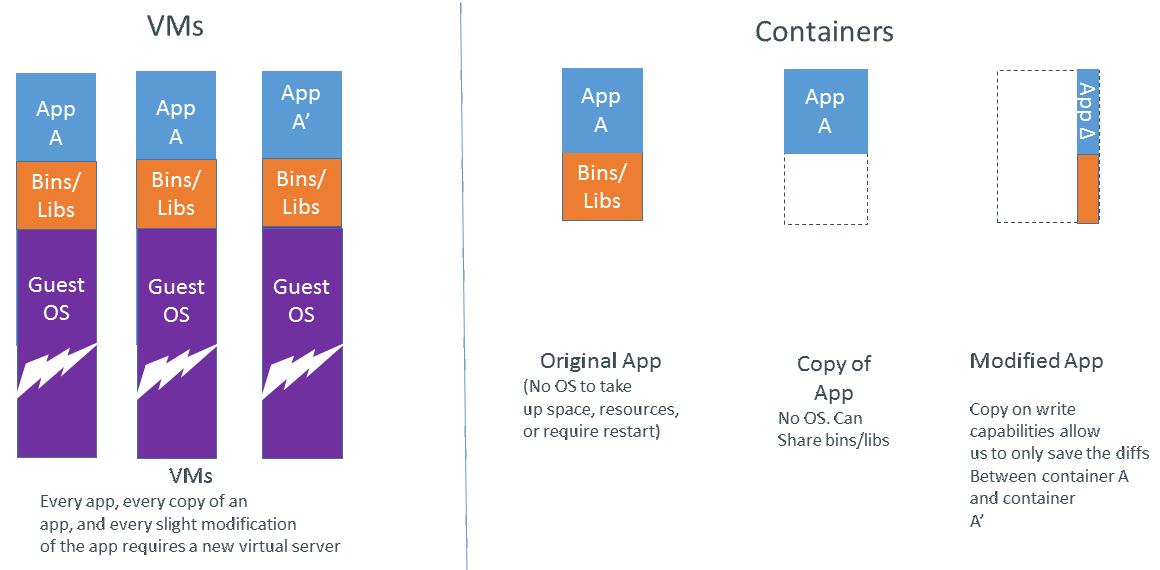
Containers vs VMs
Containers use fewer resources since they share the OS kernel, a crucial advantage in scientific computing and scientific ML, where heavy computation demands efficiency.
Digital twins can simulate real-world environments more effectively with containers, ensuring that resource allocation is optimized for simulation fidelity.
Lightweight by Design
Docker’s lightweight design makes it useful for scientific computing pipelines, where iterative and resource-heavy processes (e.g., simulations, ML model training) require quick and flexible deployment.
Digital twins benefit from Docker’s efficiency by allowing rapid iteration of simulations without the overhead of traditional virtual machines, improving performance when running real-time applications.
 .pdf
.pdf